transfer、splice
1 | //将first到last內的所有元素搬移到position 前,不包括last元素。 |
迁移过程如图: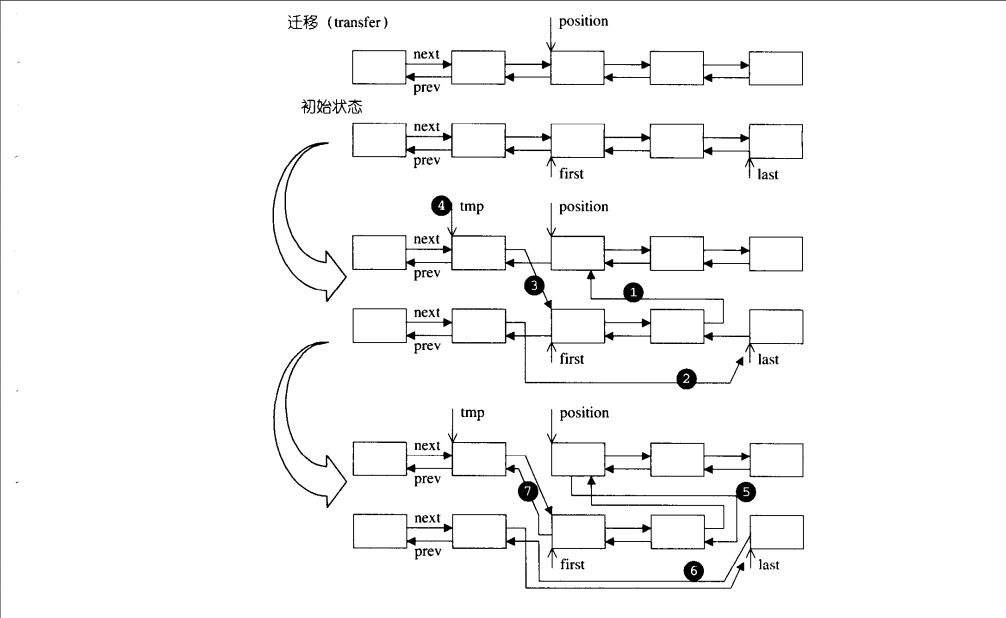
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22// 將 x 链表插入到 position 所指位置之前。x 必须不能是 *this。
void splice(iterator position, list& x)
{
if (!x.empty())
transfer(position, x.begin(), x.end());
}
// 將i所指元素插入到 position 所指位置之前。position 和i 可在同一个list。
void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator i)
{
iterator j = i;
++j;
if (position == i || position == j) return;
transfer(position, i, j);
}
// 將 [first,last) 內的所有元素插入到 position 所指位置之前。
// position 和[first,last)可指在同一个list,
// 但position不能位于[first,last)之內。
void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator first, iterator last)
{
if (first != last)
transfer(position, first, last);
}
1 | //将x合并到*this上面。两个链表都要先经过递增排序。相当于合并排序的最后一步 |
list sort
list不能采用STL sort()算法,必须使用自己的sort;因为STL sort只能接收随机流迭代器
SGI实现版:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::sort() {
if (node->next == node || link_type(node->next)->next == node) return;
list<T, Alloc> carry;
list<T, Alloc> counter[64];
int fill = 0;
while (!empty())
{
carry.splice(carry.begin(), *this, begin()); //取第一个放入carry中
int i = 0;
while(i < fill && !counter[i].empty()) //counter[i]为空则跳过
{
counter[i].merge(carry); //有序的合并到counter
carry.swap(counter[i++]);
}
carry.swap(counter[i]); //将carry中的数据交换到counter[i]中
if (i == fill) ++fill;
}
for (int i = 1; i < fill; ++i) //将数组中所有的数据合并到最后一个桶中
counter[i].merge(counter[i-1]);
swap(counter[fill-1]);
}
//两个链表交换,就是他们的node头结点交换
void swap(list<T, Alloc>& x)
{
__STD::swap(node, x.node);
}
sort的过程是一个循环归并的过程,定义一个tmp和一个list数组
假设有这样以组数: 3 5 1 2 7 6 9
1.取 3 放入carry中,此时不满足循环条件i==fill,将carry中数据换入counter[0]中,carry为空,counter[0]为{3};
2.取 5 放入carry中,carry与counter[0] merge并交换,得到counter为空,counter[1]为{3,5};
3.取 1 放如carry中,此时counter[0]为空,不进入while循环,将 1 放入 counter[0]中,counter[0]为{1};
4.去 2 放入carry中,和counter[0] merge 后又与counter[1] merge放入counter[2]中,counter[2]为{1,2,3,5}
counter[0]和counter[1]为空;
一直循环下去。。直到list为空。
然后最后面for循环将counter中的合并到最后一个中,在换给list,即完成了排序;